Optimizing Warehouse Layout For Efficiency And Safety

To improve efficiency and safety, managers should pay attention to the warehouse layout of their facilities.
A lean warehouse runs effectively and can make or break the company’s bottom line.
Warehouse optimization and efficiency play an essential role in productivity. A failure to optimize a warehouse may result in space wastage, delayed deliveries, and increased workplace hazards.
This article will discuss how you can optimize your warehouse layout, as well as enhance safety and warehouse efficiency. We will look at what a warehouse layout is, why it is important, its components, types, and how to build one.
Finally, we will explore how to optimize the warehouse layout, the common mistakes, and how to avoid them. Let’s dive in.
What is a warehouse layout, and why does it matter?
A warehouse layout should streamline operations by arranging all warehouse processes in a logical sequence. Such a layout will boost productivity and reduce operational costs. In addition, a well-executed design will provide easy access to inventory, minimize travel time, and facilitate order fulfillment.
Optimizing the warehouse layout has numerous benefits and objectives. It can help you achieve the following goals and objectives:
01. With a proper warehouse layout, you can maximize the use of space
Optimizing warehouse space is one of the most crucial objectives of an ideal warehouse layout. Using space effectively allows you to move materials quickly within a facility. You can also organize inventory, streamline processes, and keep the facility neat.
In addition, an efficient warehouse layout utilizes every inch of space to its fullest potential. Understanding your warehouse size and area is vital because it enables you to choose a layout that maximizes space use.
02. Increase productivity
Every warehouse manager seeks to enhance productivity by speeding up order picking without compromising quality. The ideal layout should eliminate errors and bottlenecks and optimize operations.
The warehouse floor plan should enable its workers to work closely with production teams to ensure all processes run smoothly and each order is fulfilled effectively.
03. Cut costs
Some warehouse layouts are more costly to create and maintain than others. Finding a cost-effective layout involves understanding what materials you are handling, what material handling equipment you need, and where to position your staff.
Once you figure out your ideal layout, you can allocate resources effectively.
According to Statista, the average cost of running a warehouse in the U.S. in 2021 was $7.91 per square foot. Having a suitable layout enables you to hire the right number of personnel and budget for warehouse maintenance.
04. Enhance safety
The warehouse layout should enable materials to move quickly through the order fulfillment process while also ensuring worker safety.
All types of hazards can occur in a warehouse. Equipment can collide, workers can fall off of unloading and loading docks, or boxes can fall.
Therefore, the layout should have all the accessories and products that keep workers safe.
Guard rails, handrails, safety bollards, and dome mirrors are some of the accessories that should be incorporated into the layout.
05. Improve warehouse management
The warehouse floor plan contributes to the larger picture of warehouse management.
It creates an environment where materials are organized, goods flow effectively between different stations, the staff is safe, orders are fulfilled on time, and stock is replenished quickly.
When all these operations run smoothly, your warehouse is set up for success.
Main components of a standard warehouse layout
There are several major areas that you must include in your warehouse layout to run effectively. These areas are used for receiving inventory, holding and organizing stock, and preparing goods for shipping. They include:
Loading and unloading area
You can either locate your loading and unloading areas outside or incorporate them into your warehouse floor plan. These are the areas that the vehicles and trucks distributing and transporting inventory have access to.
You should allow sufficient space for loading and unloading to avoid bottlenecks.

There should be enough space for loading and unloading. Image source
Where the area is incorporated into the warehouse, the docking point will enable trucks to load and unload goods directly inside the building. If the area is separate from the warehouse, you must move the goods from the docking area into the warehouse.
Reception area
The reception area – also referred to as the staging area – is where delivery, quality control, sorting, and documentation are done.
You should separate this area from all the areas of the warehouse. If there isn’t enough space allocated for the reception area, you can easily create a bottleneck in your processes.
You need to create ample space for all materials to be accurately checked, reviewed, and sorted. Once all the materials are officially received, the warehouse team determines optimal storage space.
Storage area
Storing vertically is one of the recommended techniques for optimizing space. However, not all goods can be stored this way. Stacking is also common for loads with great internal strength. Otherwise, use racking shelves for all other items.

Storing vertically is one of the recommended techniques for optimizing space.
Separating dynamic and static storage is another efficient way of utilizing space. Dynamic storage is that section where you set up the most popular items, while static storage consists of things that stay in stock longer before being shipped out.
Separating these two storage areas can help eliminate inventory mistakes and improve picking, order fulfillment time, and packing.
Picking area
These are areas where order preparation takes place, and they are not found in all warehouses. However, they are popular in shipping warehouses. Placing these areas inside or next to the storage areas reduces the time spent searching for items.
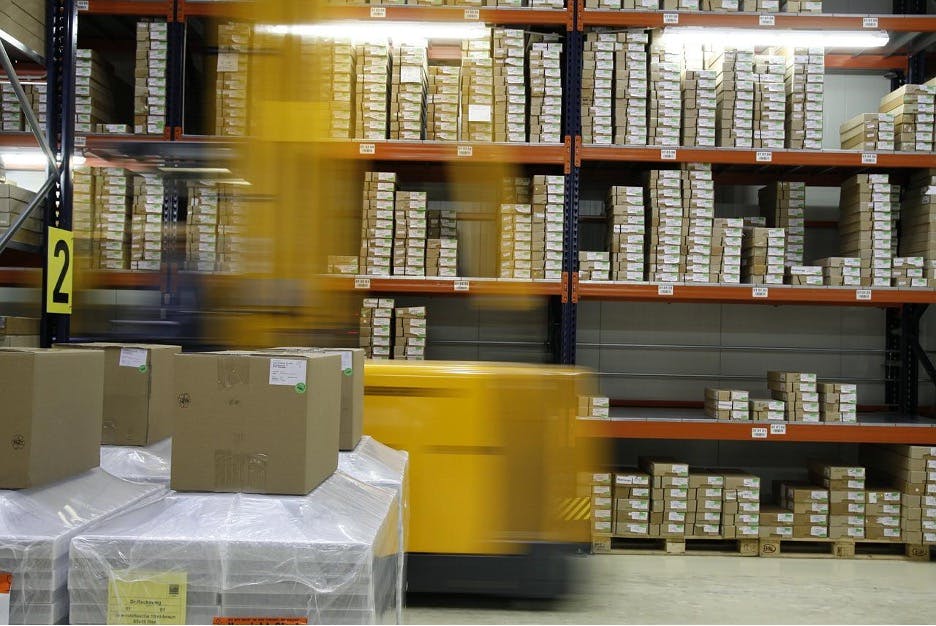

The picking area should be next to the storage area. Image source.
Picking areas allow the warehouse team to make the necessary adjustments to the orders made.
Dispatch area
This area is used for packing items prepared in the picking area. Fully prepared shipments are held in this area. Unlike the items in storage, the items in the dispatch area have been ordered and prepared.
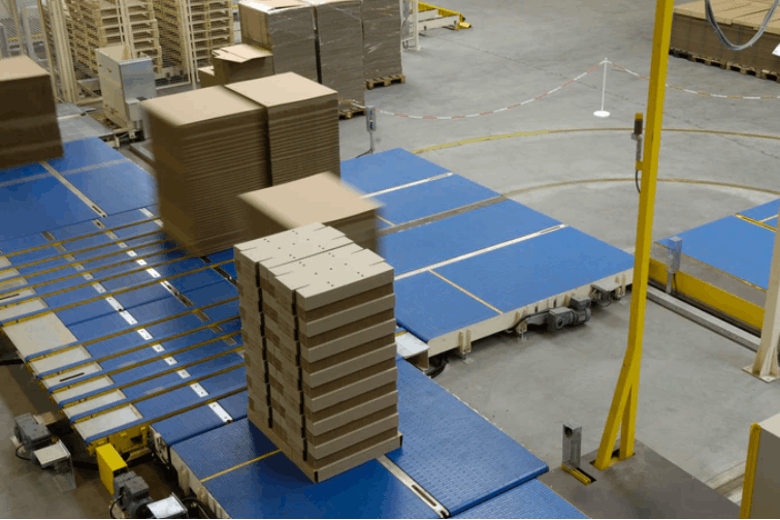

This area is used for packing items prepared in the picking area.
Dispatch should be located in an area that allows a free flow of goods from storage to the loading space. Such a layout allows a swift movement of inventory.
Offices and other facilities
You should assign a part of the warehouse to support activities. These areas are known as service areas, and they include management and general offices, bathrooms, changing rooms, dining areas, break rooms, and rooms for charging devices.
The location of service areas depends on their operational purpose and the staff that frequently uses them. For example, break rooms and offices should be placed further from noisy areas while restrooms are placed conveniently to reduce foot travel time.
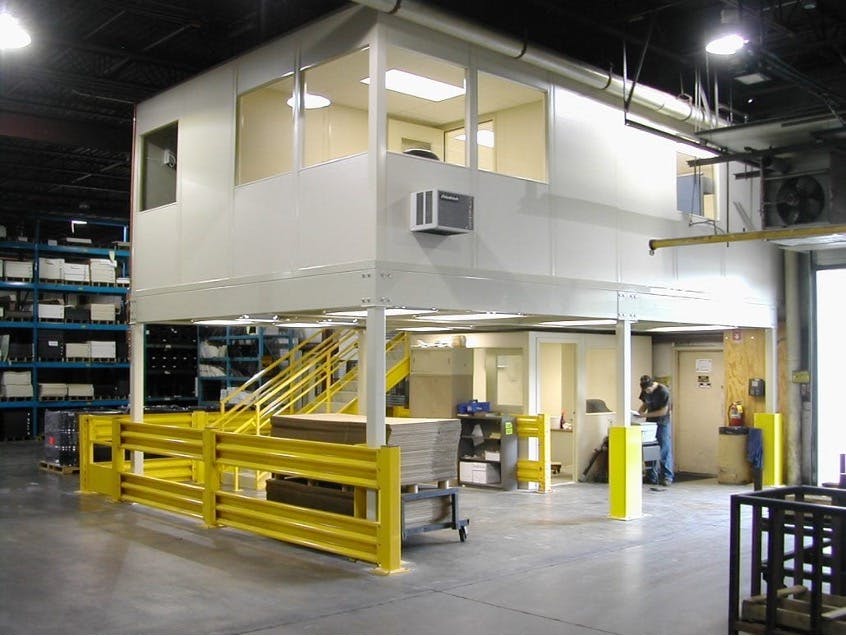

Offices should be placed further from noisy areas. Image source.
Types of warehouse layouts
It is critical to determine which warehouse layout will meet your needs. However, it will rely heavily on the available space and how materials move within the warehouse processes.
Having a suitable layout could significantly enhance efficiency and safety. But what works for one warehouse may not be ideal for yours. You should collect the necessary data and determine your goals before choosing a layout design.
There are three types of warehouse layouts, namely:
1) U-shaped warehouse layout
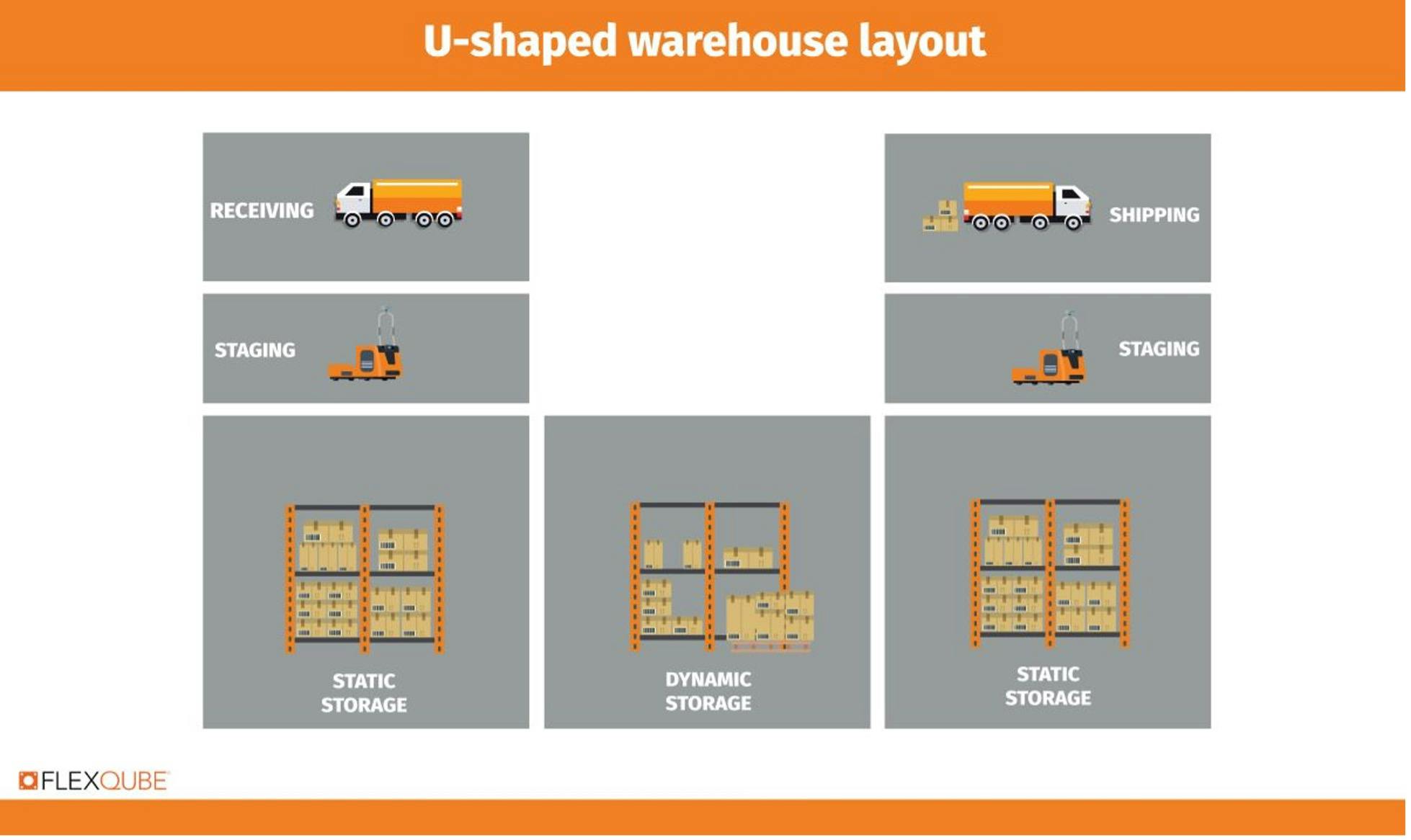
The U-shaped design is the most popular and has been recognized as the best. Its simple design makes it easy to replicate anywhere, and an ideal solution for a warehouse of any size.
This design involves arranging all the warehouse components in a semi-circular way, with shipping and receiving areas on parallel sides. The reception area comes behind loading and unloading, while picking comes behind shipping. Storage is located in the middle.
This design keeps material flow separate and streamlined and helps avoid bottlenecks.
Since the entrance and exit share the same side of the building, employees can quickly move materials between receiving and shipping. In addition, the flow of goods minimizes the space required.
However, this layout is not without its cons. Congestion can quickly occur because the receiving and shipping areas share the same side.
2) I-shaped warehouse layout
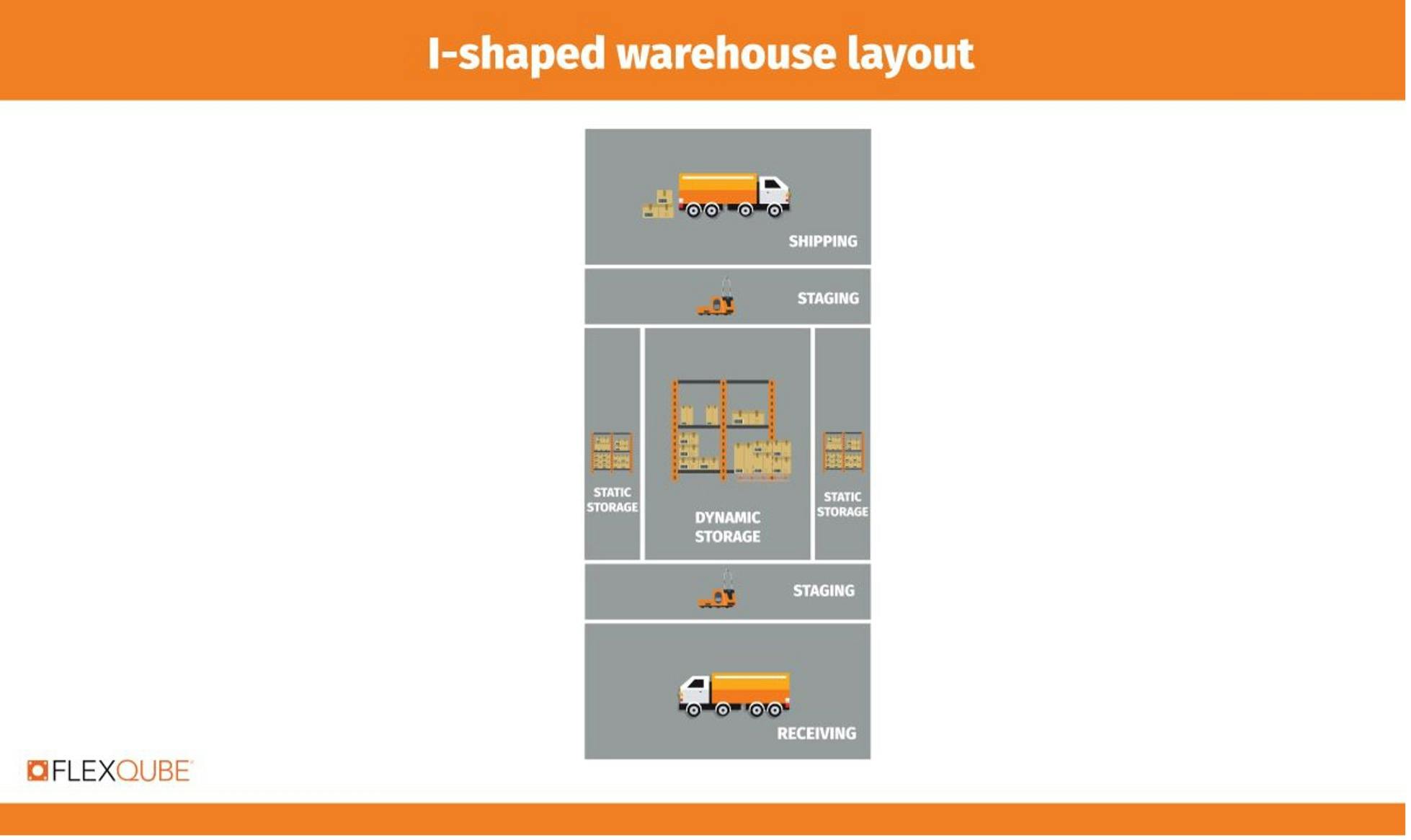
Large companies with big warehouses prefer the I-shaped design. Such corporations experience higher production volumes, and this layout is more effective because of its clear in-and-out material flow.
The I-shape layout has a straight flow from unloading/loading, receiving, storage, order picking, and shipping. It increases optimization because it utilizes the entire length of the warehouse. It also keeps similar materials in an assembly-line format and avoids back-and-forth movements, eliminating bottlenecks.
The main drawback of the I-shape layout is that the warehouse requires optimal loading and unloading areas on the two sides of the facility.
Purchasing separate docking equipment for outbound and inbound regions increases costs. Products must also travel the entire length of the warehouse to ship out.
3) L-shaped warehouse layout
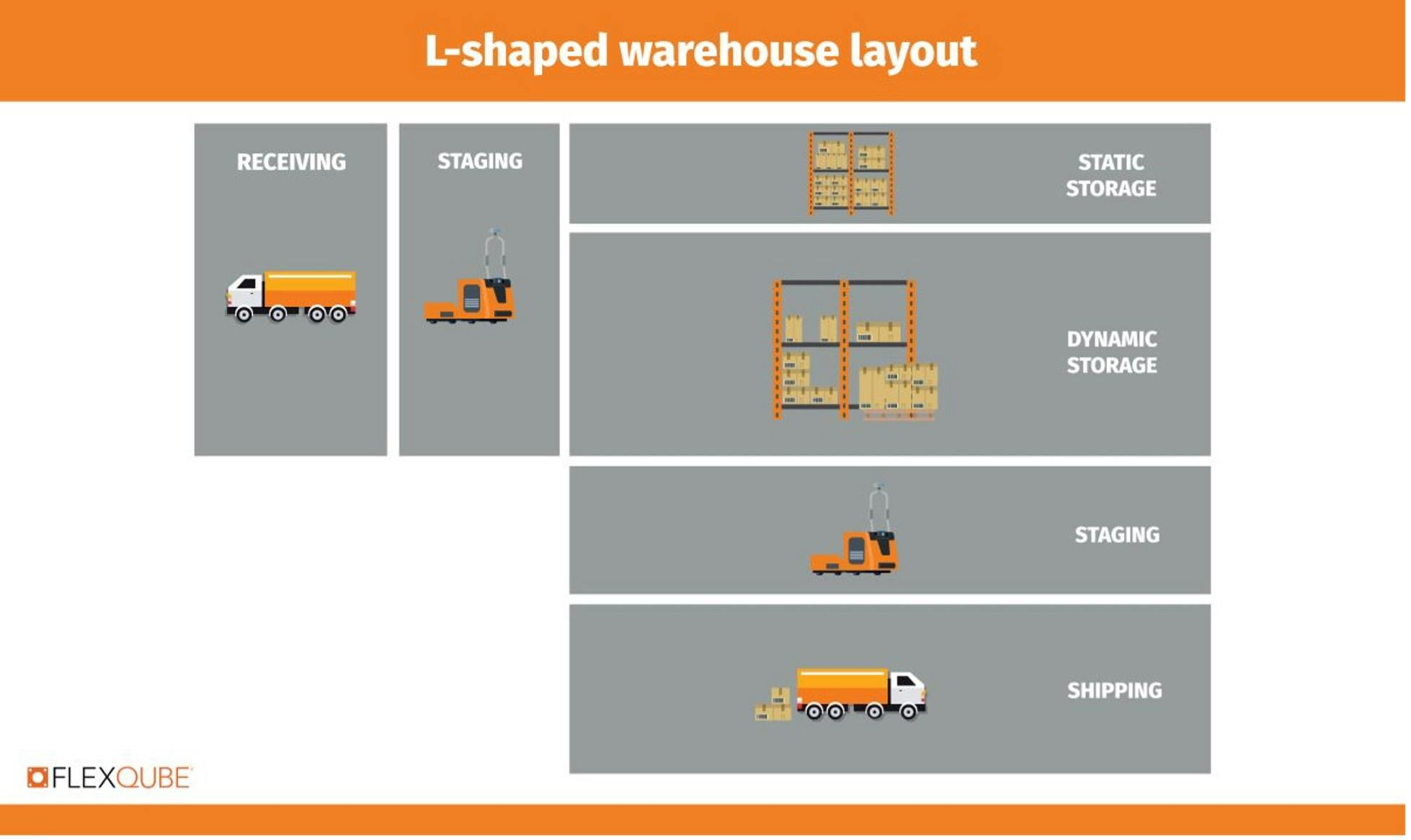
The L-shaped design is the least common and is specifically chosen to accommodate L-shaped buildings. It features the receiving space on one side and shipping on the other, at a 90-degree angle.
Both the I and L-shaped layouts offer the same benefits of enhancing warehouse optimization because goods flow in one direction, without back-and-forth movements.
The most significant drawback of this layout is the amount of space required to run the flow of materials effectively.
5 steps for building a warehouse floor plan
Building your warehouse floor plan is a massive task, and the best way of ensuring that you get it right is to have a game plan. Before launching your layout and design, consider your needs, space requirements, storage options, and equipment.
Once you have identified what you need, start designing your ideal warehouse layout.
Follow these steps:
01. Create a warehouse map
It is vital to create a visual aid that you can play around with before making any actual decisions concerning the warehouse setup. The visual aid should contain all the necessary components while utilizing every available space.

An example of a warehouse map. Image source
You can create a simple 2D blueprint using just a pen and a piece of paper. Alternatively, you can use a warehouse layout design software such as Smartdraw or AutoCAD.
Failure to get all your measurements correct can lead to problems when investing in warehouse equipment and shelves. Such equipment may not fit if your measurements are inaccurate.
Proper planning, especially a good layout blueprint, will help you avoid last-minute layout changes that can be costly. This phase also includes choosing your preferred layout.
Once you have drawn your map with measurements to scale, note all the stationary features such as supports and columns, stairways, sloping floors, office areas, bathrooms, and overhead doors. Note all these areas on your map because they will place restrictions on your warehouse floor plan.
02. Optimize your space
To optimize your layout, consider how you want to use your warehouse. Your unique needs will determine how you configure the warehouse and allocate your space.
The first step to planning your warehouse space is identifying key units that will take up most of the area. For example, in an e-commerce warehouse, the key units will be metal shelving and pallet racks.
These key units will vary based on your facility’s key goals. You should identify all your key units and place them on the warehouse map. Provide ample space for all these areas.
After planning for equipment like stock shelving, think about working areas like assembly stations. Think about how workers, goods, and materials move around these units. Consider the space needed for workers to work in the facility safely. Occupational Safety and Health Administration offers guidance on planning warehouse safety. Reserve adequate spaces for equipment and workers to transport materials safely.
Storage is a crucial factor to consider when optimizing warehouse space. Storage space is the primary concern for some facilities, especially shipping and e-commerce companies. Consider what you are storing to accurately determine the space allocated to storage areas.
03. Select your equipment
Most warehouses need storage, workspace, or material handling equipment. The size and type of your equipment come into play when planning your warehouse floor plan.
The type of materials and goods you will be handling will determine your warehouse storage and shelving units. Ensure you get the storage equipment that meets your facility’s needs.
Apart from storage equipment, you might require workspace equipment, which is also available in various options. Multi-use workbenches and tables are ideal for a variety of tasks. However, you may need specialized or dedicated workspace equipment for some functions.
Moving loads, stocks, and materials is a must in every warehouse. Therefore, you will need material handling equipment. The suitable transportation method will depend on your budget, load type, and warehouse floor layout.
Select custom and modular material handling equipment
You can purchase your warehouse equipment from a specialized dealer such as FlexQube. This ensures that you don’t have to compromise on equipment since FlexQube has a flexible concept for internal material handling carts. Instead of welding carts together you can use our concept to bolt carts and racks together. This makes them adjustable and adept for reconfigurations.
Furthermore, they can make custom modular and automated material handling equipment that fits the needs of your warehouse despite the type of layout.
04. Incorporate efficient material flow strategies
The goal of a warehouse layout is to arrange all elements to enable an efficient and safe flow of materials. Consider the following:
- The amount of time our employees spend in various locations within the warehouse.
- The elements, workspace, storage, and material handling equipment that most work will center.
- The different needs of your employees: which items should be close at hand to perform daily tasks, movement within the warehouse, and gathering items from the various locations within the warehouse.
Once you determine what needs to be done, who will do it, and the method they will use, you can predict material flow patterns. You will also need to develop ways of improving material flow within the warehouse. Think of lean material handling techniques such as milk run logistics.
05. Test your warehouse floor plan
Testing your warehouse floor plan is the last step, and it involves mocking up material flow, production zone areas, and workflow. Walk the warehouse floor like you are performing essential tasks:
Practice work functions: Carry materials, tools, or boxes while you test the warehouse design. Ensure there is adequate clearance in all directions. Roll out material handling equipment and ensure it navigates easily.
Let the employees test the floor plan: Involve employees in acting out work processes. Ensure they have enough space to perform their tasks safely.
Check hard-to-change areas: Test large spaces that will house heavy equipment. It is easier to make adjustments at this point than after installing the equipment.

Three biggest warehouse layout design mistakes and how to avoid them
- Failure to consider safety: Some warehouse managers and employees disregard safety. A safe warehouse will run smoothly and lower the costs associated with workplace injuries. All warehouses should implement a safety program that ensures material handling safety.
- Not zoning the space effectively: Failure to zone space may lead to overutilizing or underutilizing warehouse space. Warehouse space should be zoned according to the items that will be stored in the space, their size, and weight. Such zoning ensures specialized storage solutions that mitigate accidents and inventory damage.
- Failure to plan for the future: Re-structuring and expanding a warehouse layout is not only expensive but also time-consuming. Warehouse managers should plan, keeping in mind future growth.
Additional tips for optimizing your warehouse layout
After building your warehouse floor plan, you should develop deliberate strategies that will help you optimize your warehouse. Here are a few additional tips:
Define your objectives: You should clearly define your objectives before deciding on your warehouse layout. The goals should align with the overall strategy of the company.
Leverage on automation: Using warehouse management systems (WMS) ensures smooth processes and minimizes human error. Warehouse automation assists warehouses in achieving most of their goals. It covers a broad range of topics, from robotics and artificial intelligence (AI) to warehousing equipment.
Label and track inventory: Properly labeling all merchandise and materials helps eliminate errors within the warehouse. On the other hand, tracking inventory is vital in determining what you have, what you need, and what storage capacity is enough.
Regular maintenance: Consistent maintenance ensures that the warehouse layout continues to be successful. Maintenance ensures that all warehouse equipment works properly, the warehouse is neat, storage is organized, and quality control checks are conducted.
The warehouse of the future
With the demand for warehouse space growing, the future warehouse will put more pressure on efficiency and safety.
Companies will seek to get more out of the limited warehouse space.
As a result, the warehouse of the future will integrate automation seamlessly into all its processes. It will be more efficient, advanced, and safe.
It will incorporate technological advancements to improve productivity, make order fulfillment more efficient, and reduce costs.
You can start the process today by analyzing your options with a FlexQube expert technician. Tell us about your requirements and our team will help you find the right solution for your facility.

